How close is Rio de Janeiro to the equator?
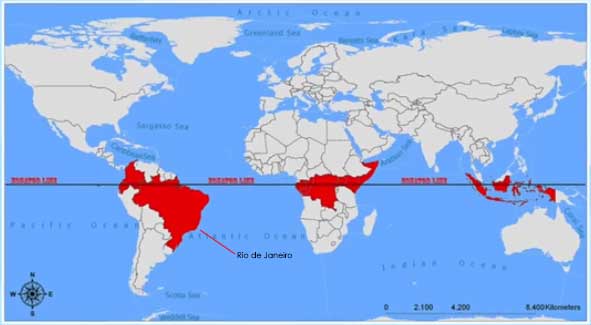
How far is Rio de Janeiro from the Equator?
When it comes to fascinating geographical facts, the question often arises: “How close is Rio de Janeiro to the equator?” As a major city in Brazil, Rio de Janeiro’s location relative to the equator is a hot topic among geography enthusiasts and travelers alike. In this article, we delve into the precise distance from Rio de Janeiro to the equator, shedding light on the city’s tropical climate and its influences.
Rio de Janeiro: A Snapshot
Before we delve into the specifics, let’s quickly understand what makes Rio de Janeiro so unique. Located in southeastern Brazil, Rio de Janeiro is not just a city but also a state. Known for its vibrant culture, breathtaking landscapes, and iconic landmarks like Christ the Redeemer and Copacabana Beach, Rio captures the heart of every visitor.
Rio de Janeiro distance from the Equator
So, how close is this Brazilian gem to the equator? In actual numbers, Rio de Janeiro is approximately 2,291 kilometers (or about 1,423 miles) away from the equator. To put it into perspective, that’s roughly the distance from New York City to the city of Dallas in the United States.
- Latitude: Rio de Janeiro is located at a latitude of approximately 22.9068° S.
- Longitude: Its longitude is approximately 43.1729° W.
Geographic Positioning of Rio de Janeiro: Understanding the Implications
The geographical positioning of Rio de Janeiro, with its intriguing distance from the equator, offers a unique perspective on this bustling city. At approximately 2,291 kilometers away from the equator, Rio isn’t exactly within a stone’s throw of this imaginary line. With a latitude of roughly 22.9068° S and a longitude of about 43.1729° W, it’s clear that Rio is considerably distanced from the equator.
Even though it’s not in close proximity to the equator, the city of Rio enjoys a relatively stable climate and consistent daylight throughout the year. This is a crucial consideration for travelers who are contemplating a visit to Rio, as it allows them to adequately prepare for the weather conditions they will encounter.
In essence, understanding Rio de Janeiro’s distance from the equator not only enriches our geographical knowledge but also gives us a better understanding of the city’s unique environment. The city’s considerable distance from the equator, contrary to what one might initially assume, significantly contributes to its charm and appeal, making it a must-visit destination for travelers.
Wrapping Up: Rio de Janeiro and the Equator
To sum up, Rio de Janeiro is approximately 2,291 kilometers away from the equator. Whether you’re a geography enthusiast or a curious traveler, understanding this aspect of Rio de Janeiro adds a new dimension to your knowledge of this vibrant city. So the next time you find yourself in Rio, you’ll appreciate not just the culture and the sights, but also the geographical significance that makes this city truly unique.
Is Rio de Janeiro south of the Equator?
Yes, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil’s renowned city, is positioned south of the Equator. Its geographical coordinates, 22.9068° S, 43.1729° W, clearly place it in the Southern Hemisphere. This location, south of the Equator, plays a significant role in shaping its tropical climate, year-round warm weather, and unique cultural experiences, making it a popular destination for tourists worldwide.
What cities in Brazil are on the Equator?
Macapá and São Gabriel da Cachoeira, located in Brazil, are unique as they are positioned directly on the Equator. This prime geographical location results in a distinct climate, characterized by consistent high temperatures and equal day-night lengths all year round. This equatorial setting influences their weather patterns, biodiversity, and local lifestyle, making them intriguing destinations for travelers seeking unusual experiences.
Which countries in South America are on the Equator?
Ecuador, Colombia, and Brazil are the three South American countries straddling the Equator. Due to their unique geographical location, they experience an equatorial climate characterized by consistently high temperatures and substantial rainfall yearly. This equatorial positioning contributes to their diverse ecosystems, lush rainforests, and exceptional biodiversity, making them a hotbed for ecological and climate studies.
Does the Equator run through Ecuador?
Absolutely, the Equator does indeed traverse Ecuador. In fact, the country’s name, Ecuador, is derived from the Spanish word for equator. This geographical feature bisects the nation into Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Remarkably, Ecuador’s capital city, Quito, is situated a mere stone’s throw away from this equatorial line. This unique positioning offers a unique equatorial climate and a rich biodiversity.
Was Ecuador named after the Equator?
Yes, the name ‘Ecuador’ is undoubtedly derived from the Spanish term for ‘Equator,’ demonstrating its unique geographic location straddling this imaginary line. This naming signifies the country’s division into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres by the Equator, a fact that greatly influences its climate, biodiversity, and overall ecological significance. Ecuador is a fascinating destination for ecological studies.
Do Equator countries have seasons?
In countries such as Ecuador, located on the Equator, there are primarily two seasons: wet and dry. This is due to the constant overhead sun, leading to high temperatures and humidity throughout the year. Unlike the typical four-season cycle, equatorial regions alternate between rainfall and dry periods, fostering unique biodiversity and ecological patterns.
Should Equator be capitalized? If so, why?
Indeed, the word ‘Equator’ should be capitalized when being used in text. As a recognized geographical feature, it’s considered a proper noun, hence the capitalization. This follows standard English grammar rules, where unique places or entities, such as the ‘Equator’, are capitalized to denote their significance and individuality. This practice helps maintain clarity and precision in written communication.